Home

Women Specific Issues

Bulky Uterus with Fibroids: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
In this Article
Women Specific Issues
Bulky Uterus with Fibroids: Understanding Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Updated on 29 September 2023



Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Shruti Tanwar
C-section & gynae problems - MBBS| MS (OBS & Gynae)
View Profile

As Vaidehi sat there in the doctor's office, her heart pounded in her chest, and my mind swirled with fear and uncertainty. The words she had just heard seemed to echo endlessly in her ears: "You have a bulky uterus with fibroid." It was a moment that changed her life forever, forcing her to confront a reality she had never imagined. The symptoms had been there for a while – the heavy and prolonged periods, the nagging lower back pain, and the constant pressure in her abdomen but she had dismissed them like most women do.
It was in that moment of vulnerability that she made a promise to herself – to embark on a journey to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition, not just for herself but for every woman who has ever felt the overwhelming burden of a bulky uterus with multiple fibroids. So, let’s join Vaidehi in her exploration of this condition.
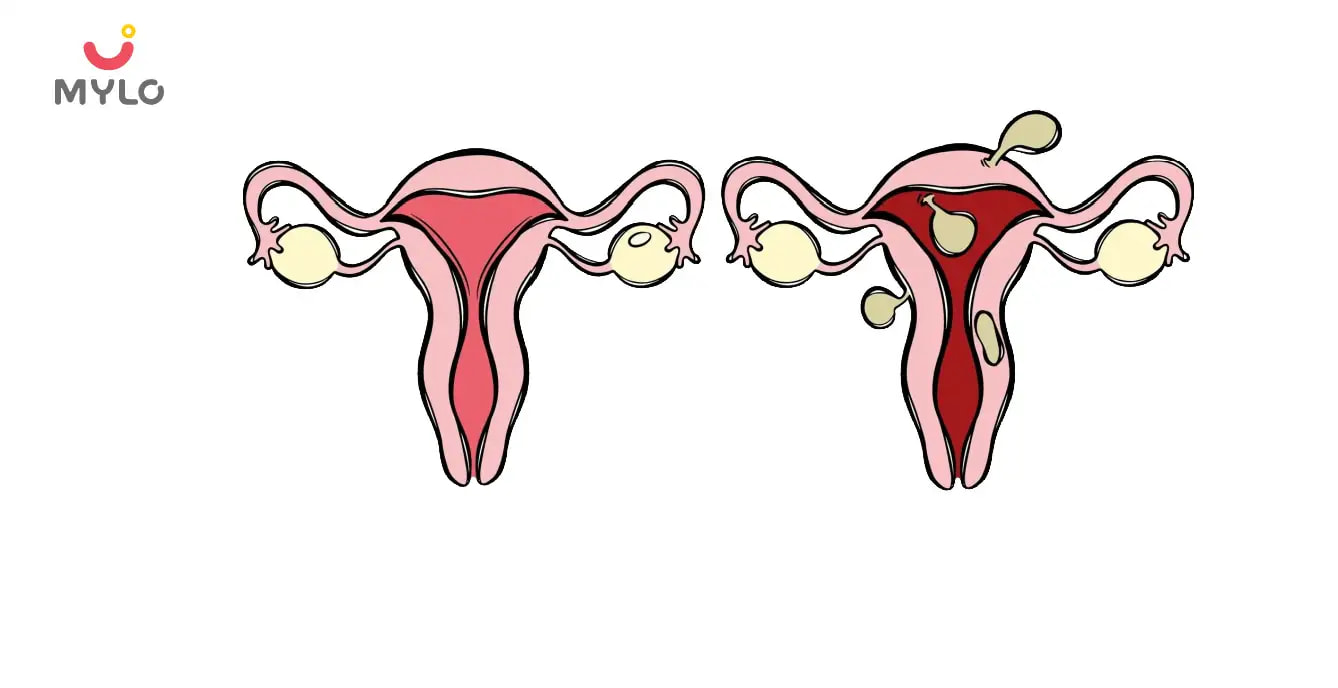
What is a Bulky Uterus with Uterine Fibroid?
A bulky uterus with fibroid means there is a presence of abnormal growths in the uterus. Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are noncancerous tumors that develop within the muscular wall of the uterus. When these fibroids grow larger, they can cause the uterus to become enlarged and bulky. The size and number of fibroids can vary from one individual to another, leading to different degrees of uterine enlargement.
What are the Causes of Bulky Uterus with Fibroid?
Let us understand some reasons or conditions that may lead to a bulky uterus with multiple fibroids or single fibroid:
1. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids themselves are a common cause of a bulky uterus. Although their exact cause is not entirely understood, hormonal factors and genetic predisposition are believed to play a role in their development.
2. Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a condition in which the endometrial tissue (the tissue that lines the uterus) grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. As a result, the uterus becomes enlarged and bulky.
3. Endometrial Hyperplasia
Endometrial hyperplasia occurs when the lining of the uterus (endometrium) becomes abnormally thickened. This condition is often caused by an excess of estrogen without the balancing effect of progesterone. Prolonged exposure to estrogen can lead to an overgrowth of the endometrial tissue, causing the uterus to become bulky.
4. Adhesions
In some cases, scar tissue known as adhesions can form inside the uterus or between the uterus and surrounding organs. These adhesions can result from previous surgeries, infections, or inflammation. As the adhesions accumulate, they can cause the uterus to become enlarged and bulky.
5. Uterine Cancer
While uterine fibroids are typically non-cancerous, it's essential to rule out the possibility of uterine cancer when encountering a bulky uterus. Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, occurs when abnormal cells develop and multiply in the lining of the uterus. This can lead to a bulky uterus and other symptoms like abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and weight loss.
You may also like : Adenomyosis Vs Endometriosis: How to Spot the Symptoms and Seek Early Intervention
What are the Symptoms of Bulky Uterus with Multiple Fibroids?
The symptoms of a bulky uterus with more than one fibroid can vary depending on the size, location, and number of fibroids present. Some common symptoms include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- An enlarged abdomen
In some cases, fibroids can cause infertility or complications during pregnancy, such as an increased risk of miscarriage or preterm labor.
You may also like : Female Fertility and Fertility Treatments: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Diagnose Bulky Uterus with Uterine Fibroid?
To diagnose a bulky uterus with intramural fibroids, healthcare professionals may use several diagnostic methods. Here are four common approaches:
1. Pelvic examination
During a pelvic examination, a healthcare provider physically examines the pelvic area to check for any abnormalities, such as an enlarged uterus or the presence of fibroids. They may also look for other symptoms like tenderness or pain.
2. Imaging tests
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, can provide detailed pictures of the uterus and help identify the presence, location, and size of fibroids. These tests can help confirm the diagnosis of a bulky uterus with multiple fibroids.
3. Transvaginal ultrasound
This type of ultrasound involves inserting a probe into the vagina to obtain more precise images of the uterus and fibroids. It can provide a closer view of the fibroids and help determine their characteristics.
4. Hysteroscopy
A hysteroscopy involves inserting a thin, lighted tube called a hysteroscope through the vagina and cervix into the uterus. This allows the healthcare provider to directly visualize the inside of the uterus and identify any fibroids or other abnormalities.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options based on individual circumstances.
Are There Any Complications Associated with a Bulky Uterus with Fibroids?
While uterine fibroids are typically noncancerous and benign, they can lead to various complications such as:
1. Altered ovarian and sexual function:
A bulky uterus with uterine fibroids can potentially affect the functioning of the ovaries and sexual organs. This can lead to hormonal imbalances and changes in sexual desire or function.
2. Subcutaneous tissue necrosis:
In rare cases, fibroids can cause the death of the surrounding subcutaneous tissue due to inadequate blood supply. This can result in tissue necrosis and may require medical intervention.
3. Expulsion of fibroid tissue
Sometimes, fibroids can become dislodged from the uterine wall and be expelled through the vagina. This can cause pain and discomfort and may require medical attention.
4. Treatment failure
In some cases, the treatment options chosen to address a bulky uterus with fibroids may not effectively alleviate symptoms or shrink the fibroids. This can lead to treatment failure and the need for alternative interventions.
5. Obstetric complications
Women with large uterine fibroids measuring more than 5 cm in diameter are at a higher risk of experiencing complications during pregnancy and childbirth. These complications may include postpartum hemorrhage and an increased risk of cesarean section, especially if the fibroids are located lower in the uterus.
Bulky Uterus with Fibroid Treatment
Treatment options can depend on various factors such as the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and the patient's desire for future fertility. The three main treatment approaches include medications, surgical procedures, and lifestyle changes.
1. Medications
Medications can help manage the symptoms associated with a bulky uterus and fibroids. Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills or hormone-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), can help regulate menstrual bleeding and reduce pain.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists may be prescribed to shrink fibroids temporarily, providing relief from symptoms. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and discomfort.
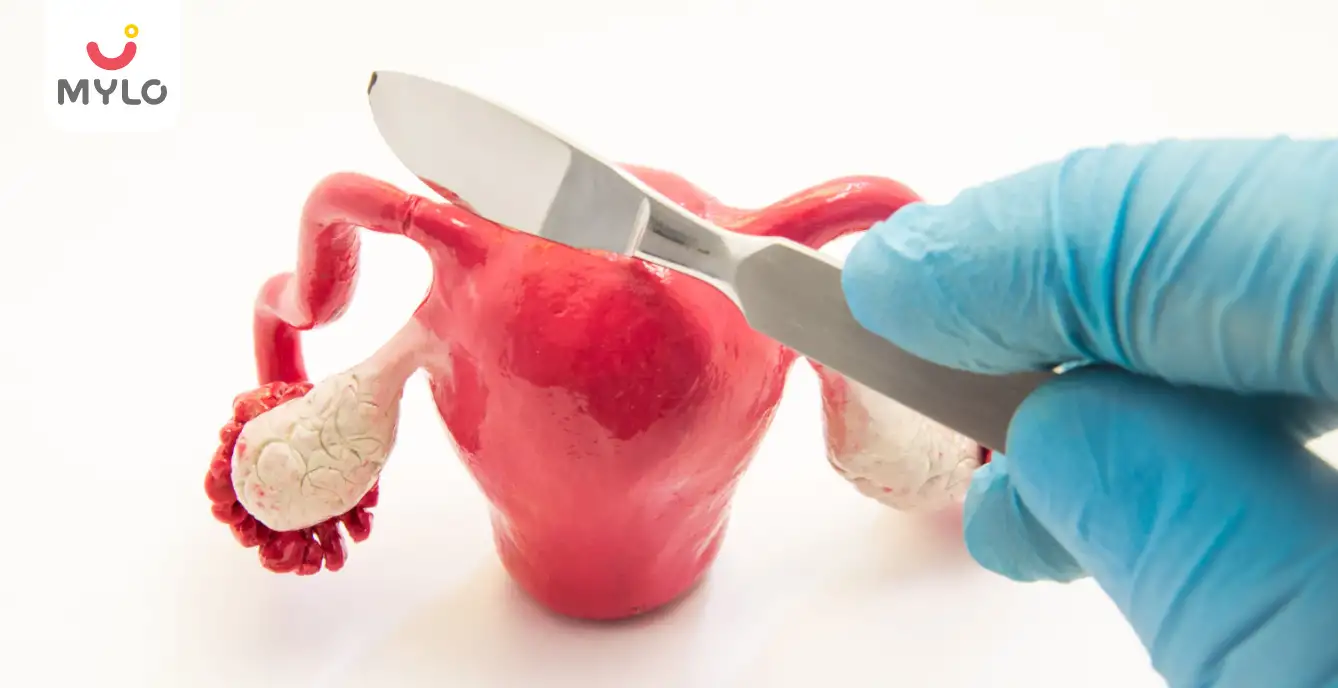
2. Surgical procedures
Surgical procedures may be considered if medications fail to provide sufficient relief or if the fibroids are causing significant complications. Minimally invasive options include laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgeries, such as myomectomy, which involves removing the fibroids while preserving the uterus.
In more severe cases, a hysterectomy may be recommended, especially for women who no longer desire fertility.
3. Lifestyle changes
Implementing certain lifestyle changes can help manage the symptoms of a bulky uterus with intramural fibroid. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can reduce the risk of fibroid growth. Managing stress levels and practicing relaxation techniques may also be beneficial.
Additionally, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and increasing intake of fruits and vegetables can promote overall uterine health.
Final Thoughts
A bulky uterus with fibroids can cause significant discomfort and impact a woman's quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial in managing this condition effectively. It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances. By exploring medications, surgical procedures, and implementing lifestyle changes, women can find relief and regain control over their health and well,
References
1. Sohn GS, Cho S, Kim YM, Cho CH, Kim MR. (2018). Working Group of Society of Uterine Leiomyoma. Current medical treatment of uterine fibroids. Obstet Gynecol Sci.
2. Khan AT, Shehmar M, Gupta JK. (2014). Uterine fibroids: current perspectives. Int J Womens Health.





Medically Reviewed by
Dr. Shruti Tanwar
C-section & gynae problems - MBBS| MS (OBS & Gynae)
View Profile


Written by
Anupama Chadha
Anupama Chadha, born and raised in Delhi is a content writer who has written extensively for industries such as HR, Healthcare, Finance, Retail and Tech.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
Related Questions
Influenza and boostrix injection kisiko laga hai kya 8 month pregnancy me and q lagta hai ye plz reply me

Hai.... My last period was in feb 24. I tested in 40 th day morning 3:30 .. That is faint line .. I conculed mylo thz app also.... And I asked tha dr wait for 3 to 5 days ... Im also waiting ... Then I test today 4:15 test is sooooo faint ... And I feel in ma body no pregnancy symptoms. What can I do .

Baby kicks KB Marta hai Plz tell mi

PCOD kya hota hai

How to detect pcos

Related Topics
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles
Medical Procedures
Tubal Recanalization: How This Procedure Can Help Restore Your Fertility
Hormones
Are FSH (Urofollitropin) Injections an Effective and Safe Fertility Treatment For You?

Baby Massage
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing a Baby Massage Oil for Summer
Reproductive health
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding a Follicle Size Growth Chart

PCOS & PCOD
Fruits for PCOS: Your Guide to Making Healthy Choices

PCOS & PCOD
Is Milk Good for PCOS: Exploring the Dairy Dilemma
- The Ultimate Guide to Using Ashokarishta for PCOS
- PCOS Pain: The Ultimate Guide to Causes and Effective Management
- 10 Best Mystery Books to Read in 2023
- 10 Best Non-Fiction Books to Read in 2023
- Is Ghee Good for PCOS: The Ultimate Guide to Benefits and Ways to Consume
- Is Curd Good for PCOS: The Ultimate Guide to Debunking Myths and Discovering Benefits
- Beetroot for PCOS: Discovering a Natural Approach to Managing Symptoms
- Soy for PCOS: Should You Eat it or Avoid It?
- Cinnamon for PCOS: Discovering the Natural Support You've Been Missing
- When Do Babies Start Walking?
- The Ultimate Guide to 4th Month Pregnancy Symptoms
- Your Guide to 2 Months Pregnant Symptoms: What to Expect
- The Ultimate Balanced Diet Chart: Your Guide to Optimal Nutrition
- Mundan Ceremony: A New Parent's Guide to Customs, Traditions and Celebrations


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN
















- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers 6512 | cloth diapers | laundry detergent 6472 | lactomama lactation granules |




