Home

Getting Pregnant

Ovulation: The Key to Maximizing Your Chances of Conception and Pregnancy
In this Article

Getting Pregnant
Ovulation: The Key to Maximizing Your Chances of Conception and Pregnancy
Updated on 13 December 2023
For many couples, starting a family is an exciting journey and a dream come true. But for some, it can be a long and challenging process. The human body is a complex machine and conception is a delicate dance that requires precise timing and a bit of luck. However, understanding ovulation can give couples a better chance of getting pregnant and make the journey a lot smoother.
In this article, we'll explore the science behind ovulation, discuss the different methods of tracking ovulation, and understand what ovulation induction is and who might benefit from it. So, whether you're just starting your journey or have been trying for a while, read on to learn how understanding ovulation can be the key to conception.
What is ovulation?
Ovulation is the process in which a mature egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube for fertilization. This occurs around 14 days before the start of the next menstrual period and lasts about 12-24 hours. The lining of the uterus thickens to prepare for a fertilized egg, and if it doesn't occur, the lining along with the egg will shed during menstruation.
How does ovulation relate to fertility?
Ovulation is a crucial factor in fertility, as it is the time when a woman's mature egg is released from the ovary and moves down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm. Understanding your menstrual cycle and tracking ovulation can help improve your chances of getting pregnant.
There is a six-day fertile window during each menstrual cycle where pregnancy is possible, with the three days leading up to and including ovulation being the most fertile. The best chance of pregnancy is when intercourse occurs 1-2 days before ovulation.
What is the role of hormones in ovulation and conception?
Hormones play a crucial role in ovulation and conception. The menstrual cycle is regulated by hormones such as luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, estrogen, and progesterone. Ovulation, which is the release of an egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube, is regulated by these hormones and occurs around 14 days before menstruation.
If sperm is present in the fallopian tube, it can fertilize the egg, leading to conception. Progesterone, in particular, is responsible for preparing the endometrium for the uterine implantation of the fertilized egg. Disruption of these hormones can lead to pathologic sequelae, affecting ovulation and potentially leading to infertility.
Ovulation Symptoms: How to Detect Them
Although ovulation occurs around the 14th day of a woman’s menstrual cycle, some women may have shorter or longer menstrual cycles or irregular periods, which makes it important for them to understand the signs of ovulation.
Understanding symptoms of ovulation day can help women track the changes in their body, know when they are most fertile and engage in unprotected sex during that period to maximise their chances of conception.
1. Clear vaginal discharge
Just before ovulation, you are likely to notice an increase in vaginal secretions which are clear and stretchy as the cervical mucus becomes clearer and slippery during ovulation.
2. Change in body temperature
The body’s temperature increases during ovulation. You can use a thermometer to keep track of your body basal temperature and look for specific patterns to emerge. You will be more fertile two to three days before your temperature rises.
3. Abdominal cramps
Ovulation pain, also known as mittelschmerz, is pelvic pain that some women experience during ovulation. It usually occurs on the side where the ovary is releasing the egg and is caused by the stretching and rupture of the follicle that releases an egg.
4. Increased sexual desire
According to several studies, women are found to have increased sexual desire during the time of ovulation. This is caused due to the rise in estradiol levels.
5. Breast tenderness
Some women may experience breast tenderness before or after ovulation. It may be confusing with the sign of pregnancy. But in both situations, it is related to a change in hormonal levels.
6. Headache or nausea
You may also experience headaches and nausea during the ovulation period. Such symptoms can be attributed to rising estrogen and progesterone levels.
7. Bloating
Hormonal shifts during ovulation, including rising estrogen levels and the release of the egg triggered by the luteinizing hormone, can cause bloating (water retention) and gastrointestinal discomfort such as slowed digestion and increased gas.
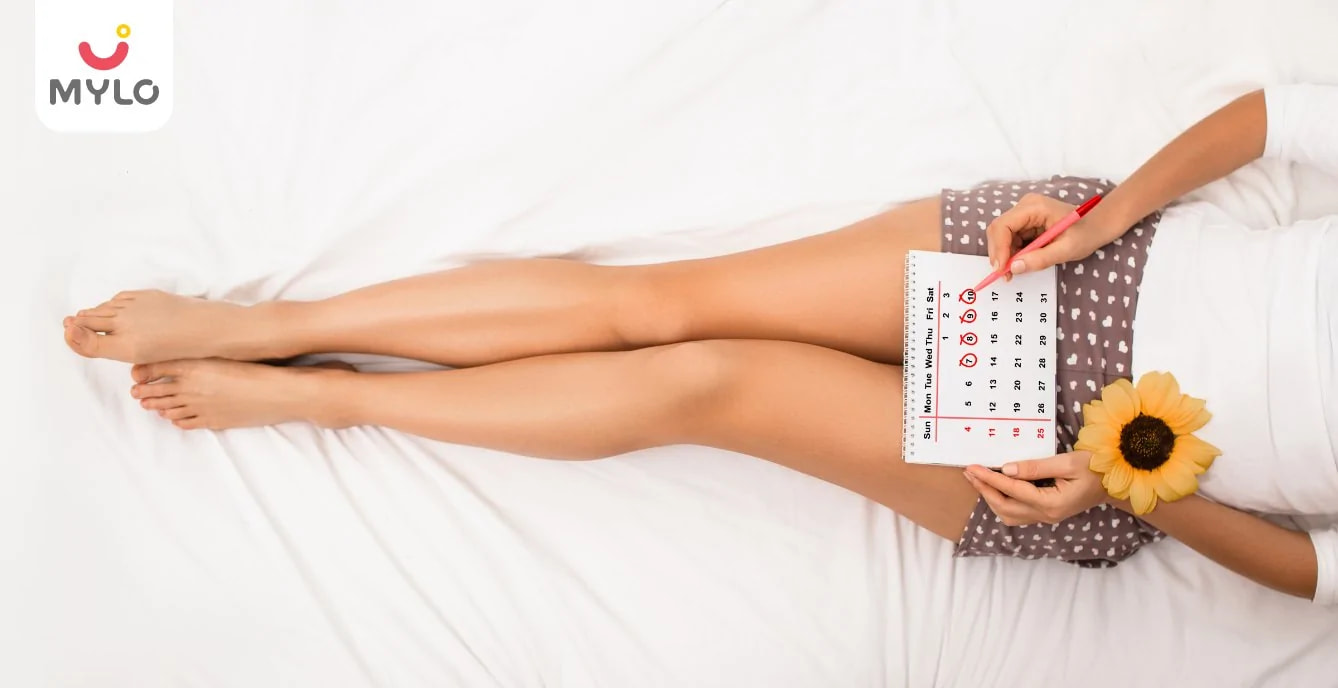
Ovulation Tracking and Fertility Aids: Calculators, Kits and Tests
Identifying symptoms of ovulation period can get confusing. To make ovulation tracking easier, there are several methods available that can help you identify when you’re ovulating. These include ovulation calculator, ovulation predictor kits, tracking your body basal temperature etc.
1. Standard Days Method
Just jot down the start date of your last menstrual cycle and ovulation will take place between the 10th-14th day from that date. This calculation is easy and simple but can’t always be accurate. Alternatively, you can use a period tracker or an ovulation calendar.
2. Ovulation Calculator
An ovulation calculator using simple details like the date of your last menstrual period and average cycle length can help tell you the exact date when you’ll be ovulating and even the days when you should have intercourse to conceive.
3. Ovulation Predictor Kits
You can also buy an ovulation kit from a pharmacist nearby and all you need to do is just pee on the stick available in the kit. The indicator will tell you whether you’re about to ovulate or not. The ovulation kit detects the surge in LH and is ninety-nine per cent accurate.
4. Track Your Temperature
Tracking your body basal temperature is another method of tracking ovulation. For this, you need to check your temperature first thing in the morning while still in bed regularly cycle after cycle. You can tell you are ovulating when this temperature is at its lowest.
5. Get to Know Your Cervix
With the help of your one or two fingers, you can check if the cervix is firm and closed because during ovulation it’ll open a bit and the mucus also becomes clear and stretchy. You may notice the discharge and remember it in your mind.
Ovulation Induction and Fertility Treatments
It’s important to note that some women may have late, irregular or absent ovulation. Late ovulation is when ovulation occurs after day 21 of a menstrual cycle due to hormonal imbalances, which can be caused by stress, thyroid disease, polycystic ovary syndrome, breastfeeding, and some medications.
Irregular ovulation refers to a condition in which a woman's menstrual cycle is inconsistent and unpredictable due to PCOS, extreme exercise, high stress levels, hyperprolactinemia, and low body weight. This means that the ovaries do not release an egg every month, which can lead to difficulty in conceiving.
Absent ovulation, also known as anovulation, is a condition where an egg does not release from the ovary during a menstrual cycle. It is responsible for about 30% of fertility problems in women. This can happen due to hormonal imbalances or other factors that interrupt the ovulation process.
You may also like: Ovulation Disorders and Their Medications
What is ovulation induction?
Ovulation induction is a medical process to stimulate ovulation in women who have irregular or absent ovulation. This treatment involves using medications to produce and release eggs, and it increases a woman's chances of becoming pregnant through sexual intercourse or by using fertility treatments.
Who might benefit from fertility treatments?
Women who are not ovulating or have irregular ovulation may benefit from ovulation induction and fertility treatments. It can help non-menopausal women who are not ovulating release eggs and possibly become pregnant. Approximately 25 per cent of female infertility cases are caused by problems with ovulation.
Types of fertility medications and procedures used to induce ovulation
Ovulation induction is always combined with intrauterine insemination (IUI) in ovulatory women and should progress only after a complete and thorough evaluation. The following fertility drugs are commonly used for ovulation induction:
1. Clomiphene citrate (Clomid)
This oral medication increases pituitary secretion of FSH and LH, stimulating ovarian follicles.
2. Letrozole (Femara)
This works by temporarily lowering a woman's level of the hormone progesterone to stimulate ovum production.
3. Human menopausal gonadotropin or hMG (Repronex, Menopur, Pergonal) and FSH (Gonal-F, Follistim)
These injectable medications are known as gonadotropins and stimulate the ovary to produce several eggs for ovulation.
4. Human chorionic gonadotropin or hCG (Profasi, Pregnyl)
This matures eggs and subsequently triggers their release during ovulation.
5. Metformin (Glucophage)
This medication is typically used in women with PCOS to treat insulin resistance and increase the chances of ovulation.
6. Bromocriptine (Parlodel) and Cabergoline (Dostinex)
These medications are used in cases of hyperprolactinemia.
Conclusion
After gaining a better understanding of ovulation, it is clear that there are many factors that can affect a woman's ability to conceive. However, armed with knowledge of the menstrual cycle, ovulation symptoms and the various methods of tracking ovulation, women and their partners can take steps to increase their chances of getting pregnant. Whether it be through lifestyle changes, fertility treatments, or simply timing intercourse correctly, there are many paths to parenthood.
References
1. Allen J. Wilcox, M.D., Ph.D., Clarice R. Weinberg, Ph.D. and Donna D. Baird, Ph.D. (1995). Timing of Sexual Intercourse in Relation to Ovulation — Effects on the Probability of Conception, Survival of the Pregnancy, and Sex of the Baby. NEJM
2. Gross BA. (1987). Natural family planning indicators of ovulation. NCBI



Written by
Ishmeet Kaur
Ishmeet is an experienced content writer with a demonstrated history of working in the internet industry. She is skilled in Editing, Public Speaking, Blogging, Creative Writing, and Social Media.
Read MoreGet baby's diet chart, and growth tips

Related Articles
RECENTLY PUBLISHED ARTICLES
our most recent articles

Fun & Humour
The Ultimate Compilation of Fancy Dress Ideas for Young Kids
Conception
How Long Does Sperm Take to Reach the Egg?

Ovulation
Pregnancy Symptoms After Ovulation Day by Day: Exploring the Daily Progression

Ovulation
Signs Ovulation is Over: Your Guide to Understanding the End of Ovulation

Stories
Top 15 Akbar and Birbal Stories for Young Kids

Abortion
How Soon After an Abortion Can You Get Pregnant?
- PCOS and Sex: Exploring Impact on Health and Debunking Common Myths
- Papaya for PCOS: Exploring the Link and How It Can Positively Impact Your Health
- How to Boost Fertility in Your 30s: The Ultimate Guide
- Anovulation Meaning Explained: What You Need to Know About Its Causes & Treatment
- Basal Body Temperature: How It Can Help You Track Ovulation?
- Ovulation Pain: Is It Normal or a Cause for Concern?
- Special Home Remedies For Gas During Pregnancy
- PCOD Problem After Marriage: Debunking Common Misconceptions and Finding Solutions
- White Discharge After Ovulation: A Normal Occurrence or Cause for Concern?
- Normal Ovary Size: How It Varies and What It Means for You
- 2024 Calendar with Holidays and Festivals of India
- After-Abortion Sex: A Guide to Physical and Emotional Wellness
- Cervical Cerclage: A Closer Look at the Procedure and Its Benefits
- The Ultimate Guide to Panchatantra Stories for Kids


AWARDS AND RECOGNITION

Mylo wins Forbes D2C Disruptor award

Mylo wins The Economic Times Promising Brands 2022
AS SEEN IN
















- Mylo Care: Effective and science-backed personal care and wellness solutions for a joyful you.
- Mylo Baby: Science-backed, gentle and effective personal care & hygiene range for your little one.
- Mylo Community: Trusted and empathetic community of 10mn+ parents and experts.
Product Categories
baby carrier | baby soap | baby wipes | stretch marks cream | baby cream | baby shampoo | baby massage oil | baby hair oil | stretch marks oil | baby body wash | baby powder | baby lotion | diaper rash cream | newborn diapers | teether | baby kajal | baby diapers | cloth diapers |








